AIM Industrial, a full-service industrial contractor based in Cambridge, Ontario, needed a better way to manage the complexity of its daily operations. From job tracking and invoicing to safety compliance and crew scheduling, the company's growing volume of work was being managed through spreadsheets, email chains, and disconnected systems.
ISU Corp partnered with AIM to design and launch a custom-built operations platform that brings their entire workflow under one roof. The software centralizes critical processes, scheduling, field operations, reporting, quoting, timesheets, and billing into a secure, scalable, cloud-based system tailored for AIM’s specific needs.
About AIM Industrial
Fast Facts:
Headquartered in Cambridge, Ontario
6 core service divisions, including Millwrighting and Custom Fabrication
Full-service shop with engineering and project management support
Awarded Toyota’s “Supplier Award of Excellence”
Trusted by major industrial clients across North America
The Challenge
AIM’s operational workflows spanned multiple departments and field crews. But their systems weren’t connected, making job tracking, employee scheduling, invoicing, and quoting slow and error-prone.
The lack of centralized visibility led to:
Inconsistent job reporting across teams
Manual and time-consuming billing processes
Disconnected timesheet and payroll tracking
Limited transparency into real-time project status
As the company grew, these inefficiencies made it harder to scale operations while maintaining quality and client responsiveness.
What AIM Needed:
A centralized operations platform to manage jobs from quote to invoice
Real-time visibility into scheduling, timesheets, and project status
Tools to automate repetitive tasks like reporting and billing
A secure, cloud-based solution accessible from office and field
Custom workflows tailored to how AIM actually runs its business
The Solution: Custom Operations Platform Built with ISU Core
ISU Corp worked closely with AIM Industrial to architect and deliver a fully customized operations platform, designed around AIM’s real-world workflows. The software was built using ISU Core as the foundation, enabling fast, flexible development of key modules.
Key Features:
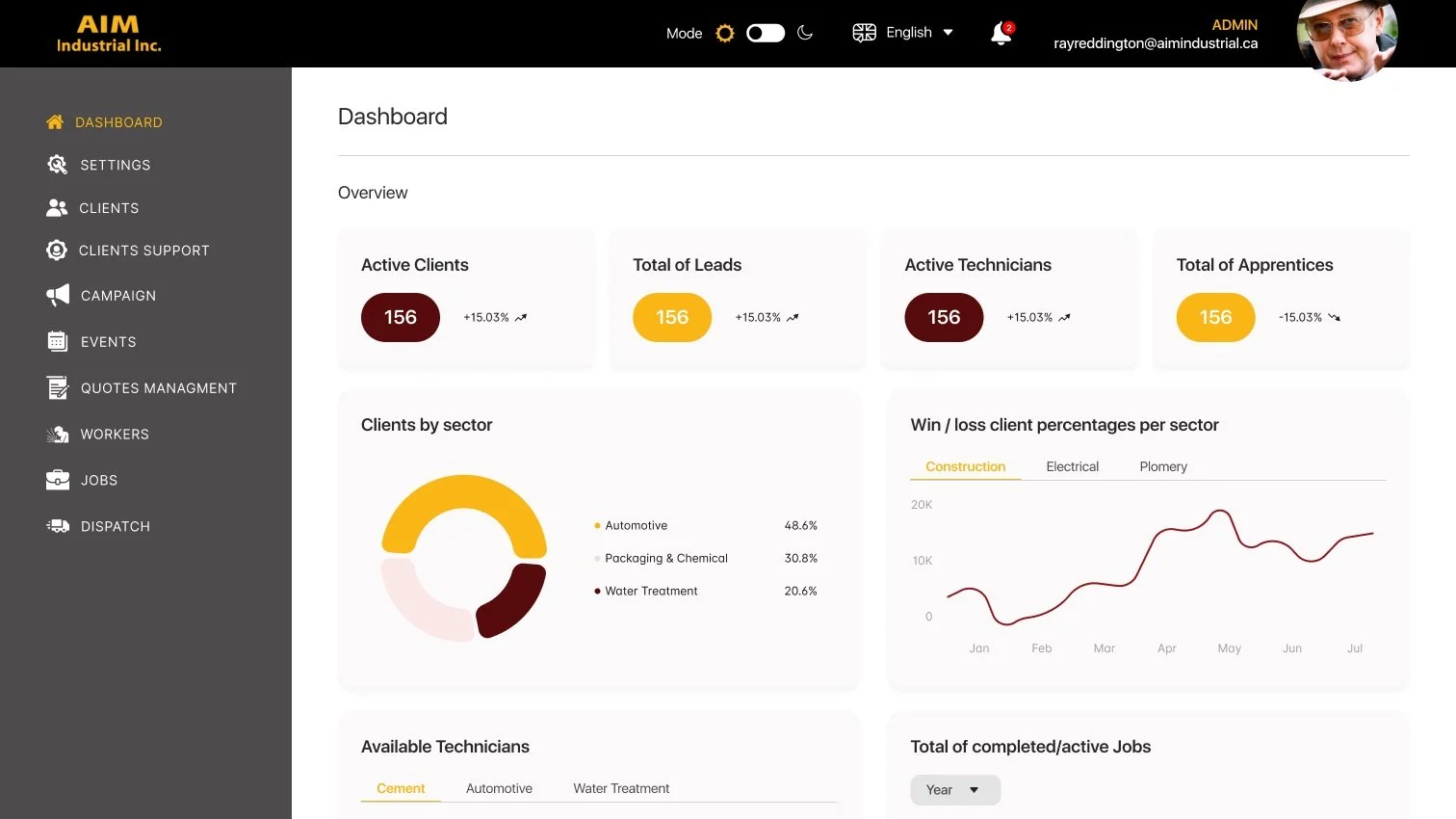
Job Scheduling & Tracking: Plan and monitor projects across departments with live status updates
Field Team Management: Assign crews, manage work orders, and capture timesheets on-site
Quoting & Invoicing Tools: Generate job quotes, log job costs, and convert them into professional invoices
Safety & Compliance Logging: Track certifications, incident reports, and jobsite safety protocols
Custom Admin Controls: Full back-office dashboard with user access, data reporting, and project search
The Results
✔ Centralized platform replacing spreadsheets and manual tools
✔ Faster job quoting, invoicing, and reporting
✔ Improved crew scheduling and project coordination
✔ Better visibility for leadership across active jobs and work history
✔ A scalable system that supports AIM’s future service expansion
The platform continues to evolve with AIM’s needs, with ISU Corp providing ongoing support and development as part of a long-term strategic partnership.
Why Custom Operations Software Matters for Industrial Companies
Industrial service providers like AIM face unique challenges: complex projects, strict compliance standards, and distributed field teams. Off-the-shelf platforms often fall short when flexibility, control, and industry-specific workflows are required.
By investing in a custom software platform built around their operations, AIM Industrial improved efficiency, accountability, and visibility across every department, without having to change how they work.
Whether you're managing jobs, crews, or compliance records, a centralized system tailored to your workflow can drive serious results.
Ready to Streamline Your Operations?
ISU Corp specializes in building custom operations platforms for industrial service companies. We help businesses like AIM digitize workflows, connect their teams, and scale with confidence.
Let’s transform your operations. Contact ISU Corp to explore how custom software can power your business from the inside out.